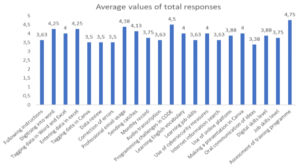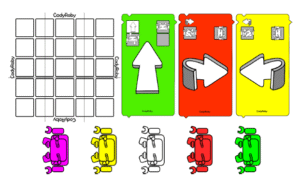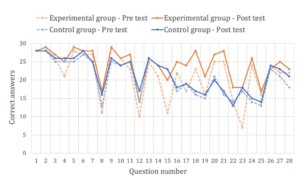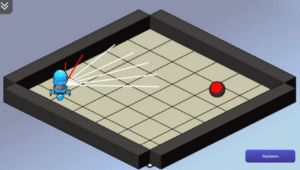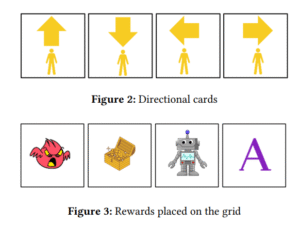
Integrating Programmable Robots to Foster Computational Thinking in Early Childhood Classrooms
Gamarra-Expósito, A., Martín-Barroso, E., & Zapata-Cáceres, M. (2025). Integrating Programmable Robots to Foster Computational Thinking in Early Childhood Classrooms. Proc. Special Issue on Innovations and Applications of Educational Robots and Robotics (EduRobotX SIG, EATEL), CEUR-WS EduRobotX.